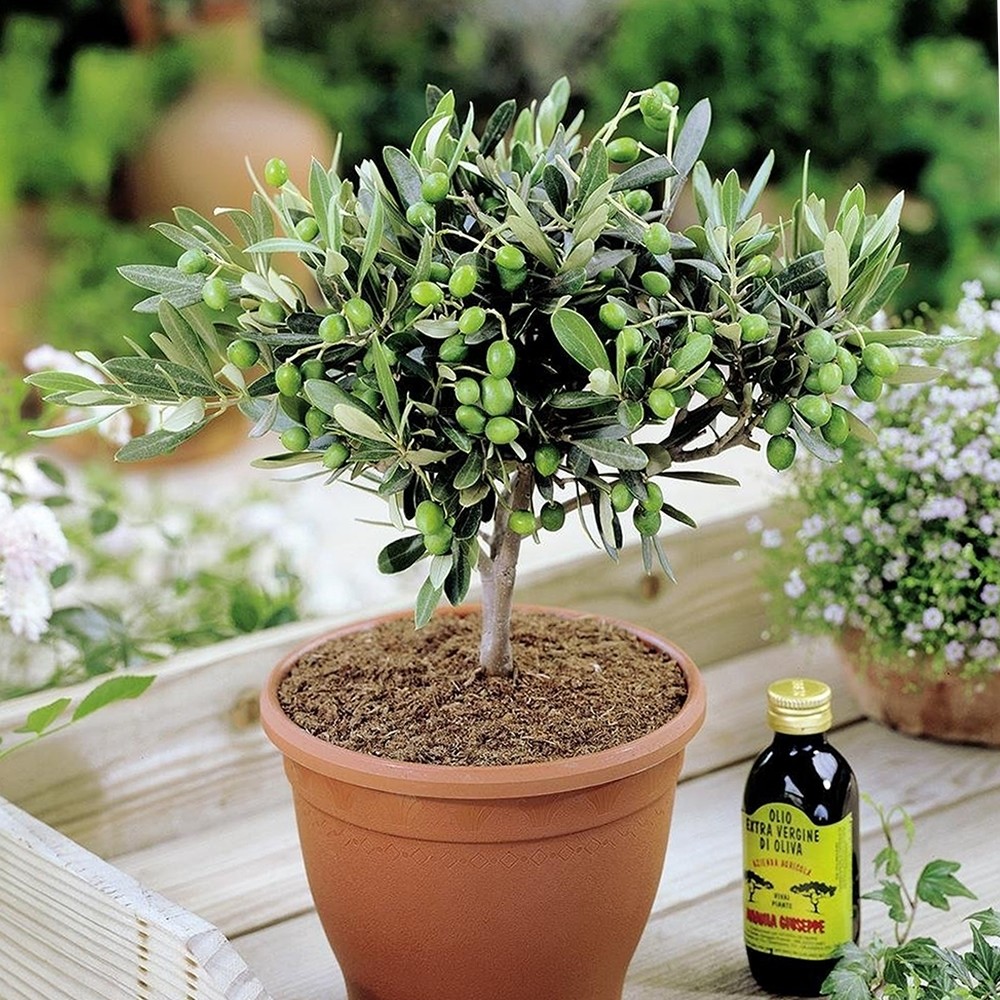
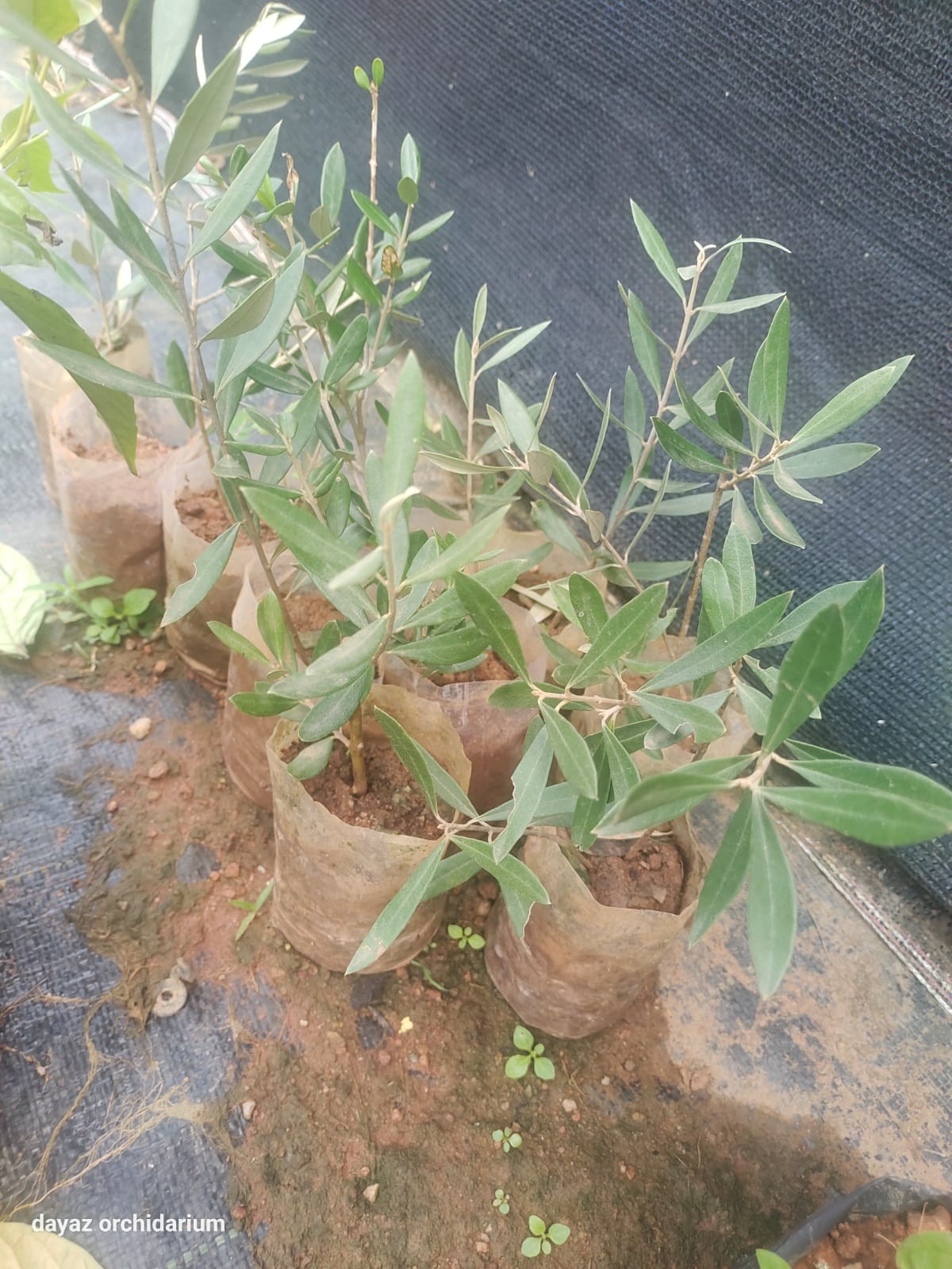
The olive plant (Olea europaea) is a small evergreen tree native to the Mediterranean region. It is widely cultivated for its fruit, olives, which are used to produce olive oil and for culinary purposes.
Characteristics:
Appearance: Olive trees have silvery-green, narrow, lance-shaped leaves. The trees can grow up to 15 meters tall but are often pruned to be more manageable.
Flowers: Small, white, fragrant flowers bloom in clusters in the spring.
Fruit: The fruit, olives, start green and turn black or dark purple when fully ripe. There are many varieties, each with different flavors and uses.
Growing Conditions:
Climate: Olive trees thrive in warm, subtropical climates. They are drought-tolerant and can withstand hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters.
Soil: Well-draining soil with a pH between 5.5 and 8.5 is ideal. Olive trees do not tolerate waterlogged conditions.
Sunlight: Full sun exposure is essential for optimal growth and fruit production.
Cultivation:
Propagation: Olive trees can be propagated from seeds, cuttings, or grafting. Cuttings are the most common method for commercial cultivation.
Watering: While drought-tolerant, young olive trees need regular watering until established. Mature trees require less frequent watering.
Pruning: Prune olive trees to remove dead or diseased wood and to shape the tree for better air circulation and sunlight penetration. This also helps in managing the height and promoting fruit production.
Care and Maintenance:
Fertilizing: A balanced fertilizer applied in early spring can support growth. Avoid excessive nitrogen, which can lead to excessive vegetative growth at the expense of fruiting.
Pest and Disease Management: Common pests include olive fruit flies and scale insects. Diseases like verticillium wilt and peacock spot can affect olive trees. Regular monitoring and appropriate treatments are necessary for healthy trees.
Harvesting:
Timing: Olives are typically harvested in the fall. The exact timing depends on the desired use—green olives for pickling are harvested earlier, while olives for oil are harvested later when they are fully ripe.
Method: Olives can be hand-picked or harvested using mechanical shakers.
Uses:
Culinary: Olives are used in a variety of dishes and are often pickled. Olive oil is a staple in cooking and is valued for its flavor and health benefits.
Nutritional Benefits: Olives and olive oil are rich in monounsaturated fats, antioxidants, and vitamins E and K, offering numerous health benefits, including heart health.